Using GitLab and Anka Build Cloud
If you are using GitLab, Veertu provides and maintains the Anka GitLab Runner. The runner connects GitLab to the Anka Cloud Controller to perform VM Instance creation and command execution through SSH into the VM Instance.
VM Template & Tag Requirements
The below list are the absolute necessities needed to execute commands in a VM through your CI and the GitLab Runner. You may have to include other dependencies depending on your needs.
- In the VM:
- Install
git - Make sure remote login is enabled (
System Preferences > Sharing).
- Install
- On the host, enable port forwarding of the VM’s 22 port using the Anka CLI. We recommend not specifying
--host-port. sudo anka suspend {VM Template name}sudo anka registry push {VM Template name} {Tag name}
Preparing the Anka GitLab Runner
These steps are based on GitLab 13.1.4; Your version/UI may differ slightly.
You can run the Anka GitLab Runner on any machine with network access to the Anka Cloud Controller, Anka Nodes, and your GitLab.
Downloading
You can find our releases on the Anka GitLab Runner GitHub.
You can then curl down the version you need for your OS and architecture:
We’ll be using a amd64 mac for our guide. However, the commands also work for Linux with slight alterations.
curl -L -o anka-gitlab-runner-v1.1.0-darwin-amd64.tar.gz https://github.com/veertuinc/gitlab-runner/releases/download/v1.1.0/anka-gitlab-runner-v1.1.0-darwin-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xzvf anka-gitlab-runner-v1.1.0-darwin-amd64.tar.gz
cp -f anka-gitlab-runner-darwin-amd64 /usr/local/bin/anka-gitlab-runner
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/anka-gitlab-runner
Confirm that the binary now exists:
❯ anka-gitlab-runner status
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=darwin pid=19465 revision=1fb7c012 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
anka-gitlab-runner: Service is not running.
Installing
When installing, ensure you’re in the directory you want used for the gitlab job’s working directory (and that the user as access/permissions to it)
# macOS
❯ anka-gitlab-runner install
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=darwin pid=39598 revision=c505cd17 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
# Linux
$ sudo anka-gitlab-runner install
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux pid=147005 revision=66bf0b24 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
FATAL: Please specify user that will run gitlab-runner service
$ sudo anka-gitlab-runner install -u testUser
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux pid=147054 revision=66bf0b24 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
success
On Linux, it will run as root and execute jobs as the user specified by the install command. This means that some of the job functions like cache and artifacts will need to execute /usr/local/bin/gitlab-runner command, therefore the user under which jobs are run needs to have access to the executable (chmod).
On macOS, the install command will place an anka-gitlab-runner.plist file into ~/Library/LaunchAgents/ (/Library/LaunchAgents if root user) so that the runner is available on restarts.
The .plist will contain --working-directory (which is set to the current location when running anka-gitlab-runner install) and --config (set to macOS: $HOME/.gitlab-runner/anka-config.toml / linux: /etc/gitlab-runner/anka-config.toml).
You can uninstall with
anka-gitlab-runner uninstall
GitLab Setup
Once the runner is installed, you can set it up as:
- A Shared Runner
- A repo’s Specific Runner
- Both
However, all of those require a Registration Token. Here are the GitLab UI locations where you can find that Token:
- Shared Runner: Admin Area > Overview > Runners (/admin/runners)
- Specific Runner: Under your repo > Settings > CI / CD > Click on Expand next to Runners
Registration
Obtaining the registration tokens can be scripted, but it requires access to the docker container:
SHARED_REGISTRATION_TOKEN="$(docker exec -i $GITLAB_DOCKER_CONTAINER_NAME bash -c "gitlab-rails runner -e production \"puts Gitlab::CurrentSettings.current_application_settings.runners_registration_token\"")"
PROJECT_REGISTRATION_TOKEN=$(docker exec -i $GITLAB_DOCKER_CONTAINER_NAME bash -c "gitlab-rails runner -e production \"puts Project.find_by_id($GITLAB_EXAMPLE_PROJECT_ID).runners_token\"")
With the token, you can now register using anka-gitlab-runner register (guided / prompts) or with --non-interactive:
anka-gitlab-runner register --non-interactive \
--url "http://anka.gitlab:8084/" \
--registration-token nHKqG3sYV4B5roRK1ZhW \
--ssh-user anka \
--ssh-password admin \
--name "localhost shared runner" \
--anka-controller-address "http://my.controller.url" \
--anka-template-uuid d09f2a1a-e621-463d-8dfd-8ce9ba9f4160 \
--anka-tag base:port-forward-22:brew-git:gitlab \
--executor anka \
--tag-list "localhost-shared,localhost,iOS"
You can find all of the options available with --help:
anka-gitlab-runner register --help
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=darwin pid=79549 revision=cc1f2751 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
NAME:
anka-gitlab-runner-darwin-amd64 register - register a new runner
USAGE:
anka-gitlab-runner-darwin-amd64 register [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
-c value, --config value Config file (default: "/Users/nathanpierce/.gitlab-runner/anka-config.toml") [$CONFIG_FILE]
--template-config value Path to the configuration template file [$TEMPLATE_CONFIG_FILE]
--tag-list value Tag list [$RUNNER_TAG_LIST]
-n, --non-interactive Run registration unattended [$REGISTER_NON_INTERACTIVE]
--leave-runner Don't remove runner if registration fails [$REGISTER_LEAVE_RUNNER]
-r value, --registration-token value Runner's registration token [$REGISTRATION_TOKEN]
--run-untagged Register to run untagged builds; defaults to 'true' when 'tag-list' is empty [$REGISTER_RUN_UNTAGGED]
--locked Lock Runner for current project, defaults to 'true' [$REGISTER_LOCKED]
--access-level value Set access_level of the runner to not_protected or ref_protected; defaults to not_protected [$REGISTER_ACCESS_LEVEL]
--maximum-timeout value What is the maximum timeout (in seconds) that will be set for job when using this Runner (default: "0") [$REGISTER_MAXIMUM_TIMEOUT]
--paused Set Runner to be paused, defaults to 'false' [$REGISTER_PAUSED]
--name value, --description value Runner name (default: "Veertu.local") [$RUNNER_NAME]
--limit value Maximum number of builds processed by this runner (default: "0") [$RUNNER_LIMIT]
--output-limit value Maximum build trace size in kilobytes (default: "0") [$RUNNER_OUTPUT_LIMIT]
--request-concurrency value Maximum concurrency for job requests (default: "0") [$RUNNER_REQUEST_CONCURRENCY]
-u value, --url value Runner URL [$CI_SERVER_URL]
-t value, --token value Runner token [$CI_SERVER_TOKEN]
--tls-ca-file value File containing the certificates to verify the peer when using HTTPS [$CI_SERVER_TLS_CA_FILE]
--tls-cert-file value File containing certificate for TLS client auth when using HTTPS [$CI_SERVER_TLS_CERT_FILE]
--tls-key-file value File containing private key for TLS client auth when using HTTPS [$CI_SERVER_TLS_KEY_FILE]
--executor value Select executor (anka or ssh) [$RUNNER_EXECUTOR]
--builds-dir value Directory where builds are stored [$RUNNER_BUILDS_DIR]
--cache-dir value Directory where build cache is stored [$RUNNER_CACHE_DIR]
--clone-url value Overwrite the default URL used to clone or fetch the git ref [$CLONE_URL]
--env value Custom environment variables injected to build environment [$RUNNER_ENV]
--pre-clone-script value Runner-specific command script executed before code is pulled [$RUNNER_PRE_CLONE_SCRIPT]
--pre-build-script value Runner-specific command script executed after code is pulled, just before build executes [$RUNNER_PRE_BUILD_SCRIPT]
--post-build-script value Runner-specific command script executed after code is pulled and just after build executes [$RUNNER_POST_BUILD_SCRIPT]
--debug-trace-disabled When set to true Runner will disable the possibility of using the CI_DEBUG_TRACE feature [$RUNNER_DEBUG_TRACE_DISABLED]
--shell value Select bash, cmd or powershell [$RUNNER_SHELL]
--custom_build_dir-enabled Enable job specific build directories [$CUSTOM_BUILD_DIR_ENABLED]
--cache-type value Select caching method [$CACHE_TYPE]
--cache-path value Name of the path to prepend to the cache URL [$CACHE_PATH]
--cache-shared Enable cache sharing between runners. [$CACHE_SHARED]
--cache-s3-server-address value A host:port to the used S3-compatible server [$CACHE_S3_SERVER_ADDRESS]
--cache-s3-access-key value S3 Access Key [$CACHE_S3_ACCESS_KEY]
--cache-s3-secret-key value S3 Secret Key [$CACHE_S3_SECRET_KEY]
--cache-s3-bucket-name value Name of the bucket where cache will be stored [$CACHE_S3_BUCKET_NAME]
--cache-s3-bucket-location value Name of S3 region [$CACHE_S3_BUCKET_LOCATION]
--cache-s3-insecure Use insecure mode (without https) [$CACHE_S3_INSECURE]
--cache-gcs-access-id value ID of GCP Service Account used to access the storage [$CACHE_GCS_ACCESS_ID]
--cache-gcs-private-key value Private key used to sign GCS requests [$CACHE_GCS_PRIVATE_KEY]
--cache-gcs-credentials-file value File with GCP credentials, containing AccessID and PrivateKey [$GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS]
--cache-gcs-bucket-name value Name of the bucket where cache will be stored [$CACHE_GCS_BUCKET_NAME]
--preparation-retries value Set the amount of preparation retries for a job (default: "0") [$PREPARATION_RETRIES]
--ssh-user value User name [$SSH_USER]
--ssh-password value User password [$SSH_PASSWORD]
--ssh-host value Remote host [$SSH_HOST]
--ssh-port value Remote host port [$SSH_PORT]
--ssh-identity-file value Identity file to be used [$SSH_IDENTITY_FILE]
--anka-controller-address value Anka Cloud Controller address (example: http://anka-controller.mydomain.net[:8090]) [$CONTROLLER_ADDRESS]
--anka-template-uuid value Specify the VM Template UUID [$TEMPLATE_UUID]
--anka-tag value Specify the Tag to use [$TAG]
--anka-node-id value Specify the Node ID to run the job (you can find this in your Controller's Nodes page) [$NODE_ID]
--anka-priority value Set the job priority [$PRIORITY]
--anka-group-id value Run on a specific Controller Node group [$GROUP_ID]
--anka-root-ca-path value Specify the path to your Controller's Root CA certificate [$ROOT_CA_PATH]
--anka-cert-path value Specify the path to the GitLab Certificate (used for connecting to the Controller) (requires you also specify the key) [$CERT_PATH]
--anka-key-path value Specify the path to your GitLab Certificate Key (used for connecting to the Controller) [$KEY_PATH]
--anka-controller-http-headers value In JSON format, specify headers to set for the HTTP requests to the controller (quotes must be escaped) (example: { \"HOST\": \"testing123.com\", \"CustomHeaderName\": \"test123\" }) [$CONTROLLER_HTTP_HEADERS]
--anka-skip-tls-verification Skip TLS Verification when connecting to your Controller [$SKIP_TLS_VERIFICATION]
--anka-keep-alive-on-error Keep the VM alive for debugging job failures [$KEEP_ALIVE_ON_ERROR]
To unregister, you can use
anka-gitlab-runner unregister -n "localhost shared runner"
You should now see the runner in your GitLab:
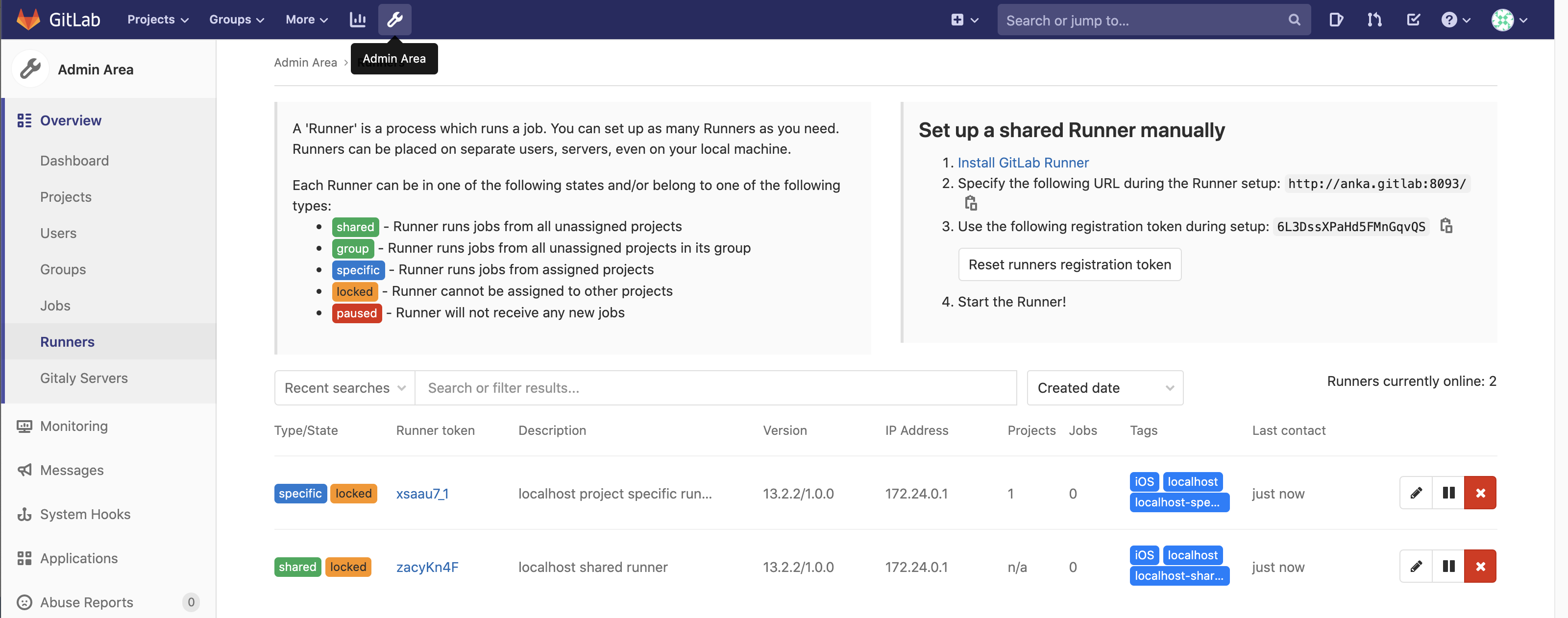
You can now start the anka-gitlab-runner:
❯ anka-gitlab-runner start
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=darwin pid=36048 revision=66bf0b24 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
executed
Ensure that GitLab shows just now under the Last contact column.
Using our Docker images
When executing docker run, any arguments included are used as options for anka-gitlab-runner register --non-interactive:
❯ docker run -ti --rm veertu/anka-gitlab-runner-amd64 --help
Updating certificates in /etc/ssl/certs...
0 added, 0 removed; done.
Running hooks in /etc/ca-certificates/update.d...
done.
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux pid=705 revision=cc1f2751 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
NAME:
anka-gitlab-runner register - register a new runner
USAGE:
anka-gitlab-runner register [command options] [arguments...]
OPTIONS:
-c value, --config value
. . .
We run
update-ca-certificateseach time you start the container. You can add a volume to mount in your certificates if needed.
You use the same non-interactive arguments that we mentioned in the Registration section when executing the binary (but without --non-interactive):
❯ docker run -ti --rm veertu/anka-gitlab-runner-amd64 --url "http://anka.gitlab:8084/" --registration-token nHKqG3sYV4B5roRK1ZhW --ssh-user anka --ssh-password admin --name "localhost shared runner" --anka-controller-address "https://anka.controller:8080/" --anka-template-uuid d09f2a1a-e621-463d-8dfd-8ce9ba9f4160 --anka-tag base:port-forward-22:brew-git:gitlab --executor anka --anka-root-ca-path /Users/nathanpierce/anka-ca-crt.pem --anka-cert-path /Users/nathanpierce/anka-gitlab-crt.pem --anka-key-path /Users/nathanpierce/anka-gitlab-key.pem --clone-url "http://anka.gitlab:8084" --tag-list "localhost-shared,localhost,iOS"
Updating certificates in /etc/ssl/certs...
0 added, 0 removed; done.
Running hooks in /etc/ca-certificates/update.d...
done.
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux pid=705 revision=cc1f2751 version=13.2.2/1.0.0
Running in system-mode.
Registering runner... succeeded runner=nHKqG3sY
Updated: /etc/gitlab-runner/anka-config.toml
Feel free to start anka-gitlab-runner, but if it's running already the config should be automatically reloaded!
Runtime platform arch=amd64 os=linux pid=705 revision=7b532a90 version=12.10.0/1.0-rc1
Starting multi-runner from /etc/gitlab-runner/anka-config.toml... builds=0
Running in system-mode.
Configuration loaded builds=0
listen_address not defined, metrics & debug endpoints disabled builds=0
[session_server].listen_address not defined, session endpoints disabled builds=0
When you stop or exit the container, it will automatically unregister it from your GitLab.
Answers to Common Questions
-
Long running jobs will fail due to the default SSHD configuration within macOS. You can set
ClientAliveIntervalandClientAliveMaxCountin the/etc/ssh/sshd_configfile of the VM to address this. -
We recommend this Stackoverflow post to understanding runner concurrency and limits
-
Environment variables such as
$RUNNER_LIMITrequire you register the runner with a template file. They will not work when set on the CLI when registering. -
The gitlab-runner’s default concurrency (amount of jobs that can run in the runner at once) setting in your
~/.gitlab-runner/anka-config.tomlis set toconcurrent = 1. It’s typical for customers to need to increase this value. -
Your gitlab job will target specific runners tags. All tags on a given job have to be met by the runner.
-
You can override the default VM Template, Tag, and targeted node group using environment variables:
ANKA_TEMPLATE_UUID,ANKA_TAG_NAME, andANKA_NODE_GROUPtest: tags: - localhost-shared stage: test variables: ANKA_TEMPLATE_UUID: "c0847bc9-5d2d-4dbc-ba6a-240f7ff08032" ANKA_TAG_NAME: "base" ANKA_NODE_GROUP: "larger-vm-pool" script: - hostname - echo "Echo from inside of the VM!" -
You can also override the HTTP headers used when communicating with the controller:
/tmp/anka-gitlab-runner-darwin-amd64 register --non-interactive \ --url "https://gitlab.url.net/" \ --registration-token <REDACTED> \ --ssh-user anka \ --ssh-password admin \ --name "mobile-dev-4 via IP and HOST header" \ --anka-controller-address "http://10.34.7.167" \ --anka-template-uuid 21d57182-c124-4b2b-afd5-d3c371c1b5c7 \ --anka-tag base:port-forward-22:brew-git:gitlab \ --executor anka \ --anka-controller-http-headers "{ \"HOST\": \"anka-controller.url.net\" }" \ --clone-url "https://gitlab.url.net/" \ --tag-list "anka-poc" -
If you see “Missing anka-gitlab-runner. Uploading artifacts is disabled” at the end of jobs that have archiving enabled, you need to install the anka-gitlab-runner in your VM Template/Tag.
-
We’ve defaulted preparation (requesting a VM from the Controller) retries to 0, but you can modify this using:
--preparation-retries value Set the amount of preparation retries for a job (default: "0") [$PREPARATION_RETRIES] -
The
anka-gitlab-runneris independent and doesn’t conflict with the regulargitlab-runnerif they’re running on the same machine. -
We use slightly modified versions of the original
gitlab-runnertests (they didn’t pass when we forked 12.10.0). -
If your controller goes down, the runner will retry the HTTP/API calls for several minutes until finally throwing an error.