Understanding VM Networking
Prerequisites
- You’ve installed the Anka Virtualization package
- You’ve got an active license
- You’ve created your first VM Template
- You understand how to start and access your VM
- You grasp how to modify VM settings, like network-card
By default, we use Apple’s VMNET interface for networking. We also configure the network service as “Using DHCP”.
Anka VMs, by default, use a shared networking configuration with the host. It’s a kind of NAT + DHCP. Every time you start/resume a VM, it gets assigned an IP that you can see with sudo anka show {vmNameOrUUID} command.
SSH access (“Remote Login”) is enabled by default on Anka VMs.
Within the VM, you can find an IP assigned to the host which can be used to ssh or transfer files out. To determine which IP is assigned to the host, execute
ipconfig getoption en0 server_identifier(typically192.168.64.1for shared network mode and192.168.128.1for host network mode)
Changing the network configuration for Anka VMs
> sudo anka modify 12.0.1 set network-card --help
Usage: anka modify set network-card [OPTIONS] [INDEX]...
Modify network card settings
Options:
-t, --type [shared|host|bridge|disconnected]
-b, --bridge TEXT host interface name to bridge with
-m, --mac TEXT specify fixed MAC address
-n, --no-mac deassign fixed MAC address
--direct-mac / --no-direct-mac expose --mac externally
-v, --vlan INTEGER assign VLAN ID
-c, --controller [anet|virtio-net]
set controller
--local / --no-local enable (default)/disable inter-VM and VM-host communication
--help Display usage information
WiFi interfaces are not supported yet
❯ anka describe 11.0.1
. . .
network_cards
+------------+--------+--------+-----------+
| pci_slot | type | mode | pci_id |
+============+========+========+===========+
| 28 | anet | shared | 538975646 |
+------------+--------+--------+-----------+
. . .
❯ anka modify 11.0.1 set network-card 0 -t bridge
❯ anka describe 11.0.1
. . .
network_cards
+------------+--------+--------+-----------+
| pci_slot | type | mode | pci_id |
+============+========+========+===========+
| 28 | anet | bridge | 538975646 |
+------------+--------+--------+-----------+
. . .
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
shared |
The default network type operating as NAT + DHCP. Every VM after the start/resume gets an IP address assigned by the internal DHCP server in range 192.168.64.2 - 192.168.64.254. Programs inside a VM can access external networks (outside the host) and the internet directly. Also, other VMs on the host are also accessible.
|
host |
It is very similar to the shared one, but the VM get IP addresses from range 192.168.128.2 - 192.168.128.254 and can’t access external networks outside of the host. |
bridge |
The Bridged type will cause the VM to show in the network as an individual device and receive a unique IP separate from the host.
|
disconnected |
The VM will have a disconnected network cable. |
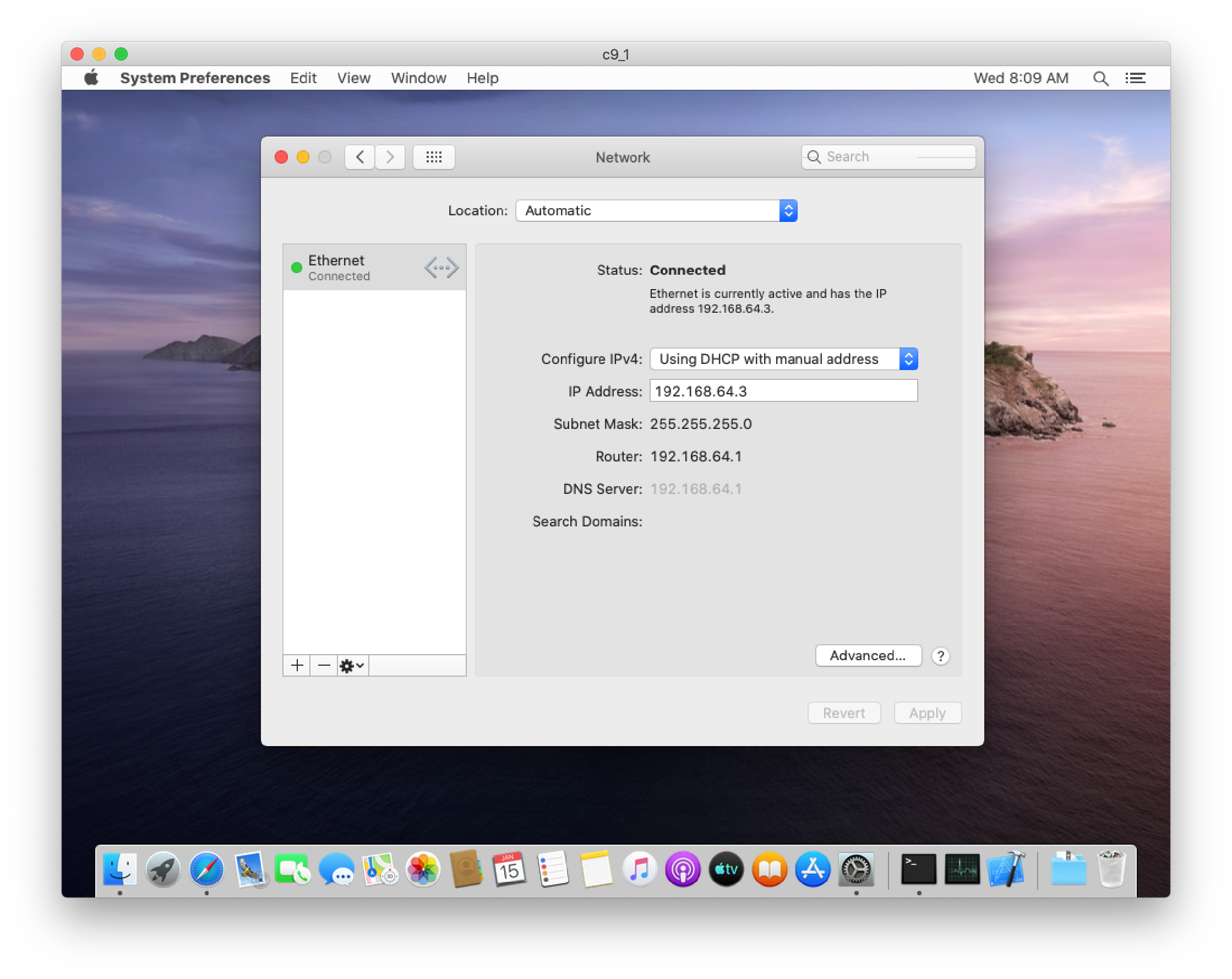
Assigning a Static IP
Anka CLI version 2.2 and greater supports Static IP on VMs running on Catalina hosts (the guest OS can be any supported macOS version):
MAC Addresses
Anka will dynamically assign MAC addresses to your VM. In Catalina and higher, you can assign custom MAC Addresses with the anka modify set network-card --mac option.
Be aware that if you clone your VM Template with a specific MAC, both VMs cannot run at the same time
Dynamic MAC Addresses are not guaranteed to be unique, though, reuse/collision is highly unlikely.
In Mojave or older macOS versions: Even if a custom MAC is set, Apple’s VMNET doesn’t recognize it on the network outside of the VM. We do a translation from the custom MAC to the one VMNET assigns. This causes the external to VM network to see the VMNET MAC, but inside of the VM you’ll see the custom MAC.
If a MAC address isn’t specified in the VM config, it treated as dynamic and Anka handles such cases for suspended VMs.
What’s next?
FAQs
- Should your Firewall software be blocking VM networking, you need to whitelist the
ankanetdprocess.